Corporate Transformation of Indonesia’s Pulp and Paper Sector

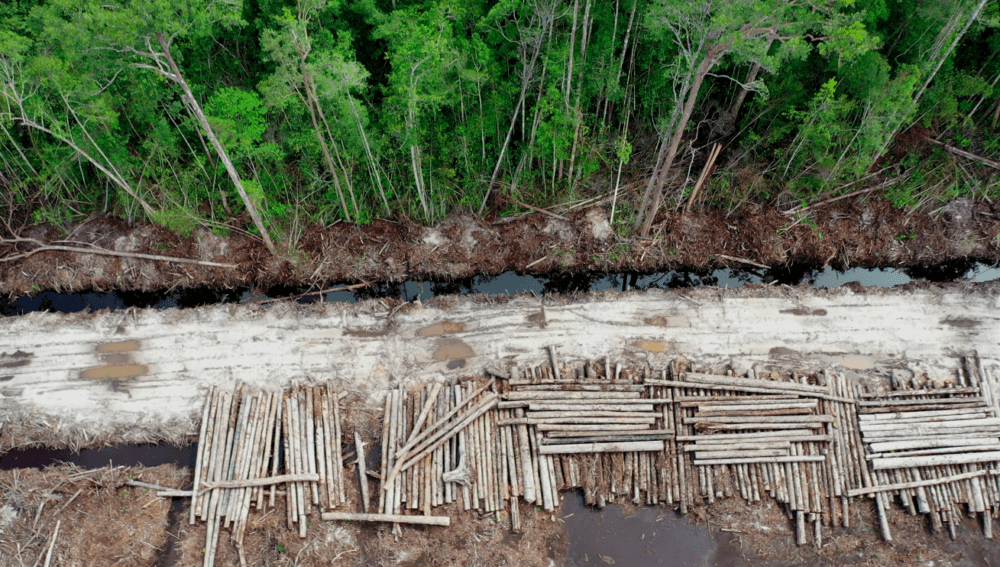
Indonesia is a top 10 global producer of pulp and paper. The raw material for this industry primarily comes from industrial tree plantations (hutan tanaman industry or HTI), the second largest plantation sector in Indonesia after oil palm and covering over 10 million hectares of land in Indonesia. Industrially grown trees are not only used for the production of pulp and paper, but also for timber products and energy generation.
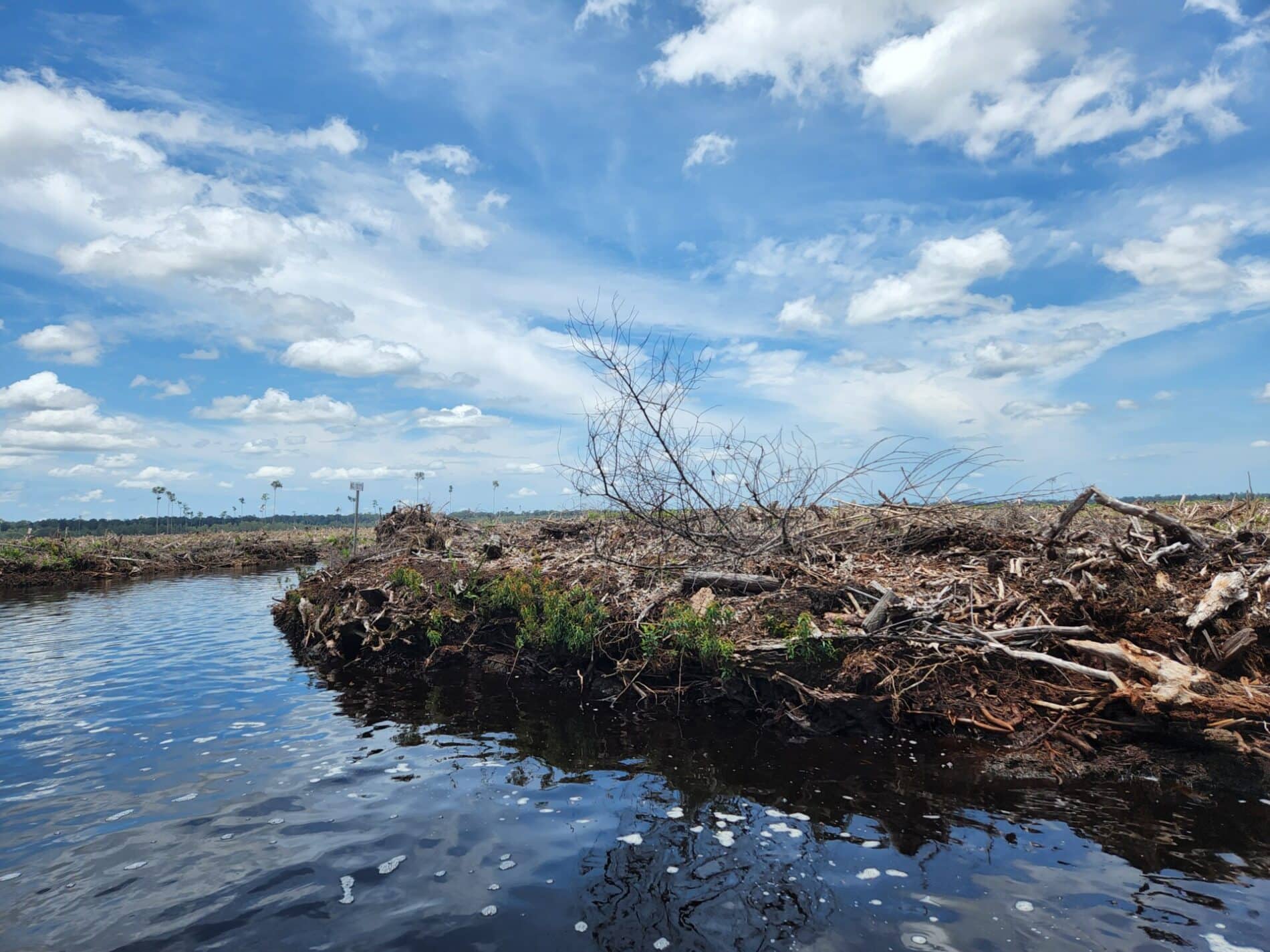
Indonesia’s pulp and paper sector faces a number of sustainability challenges. These include deforestation, the degradation of peatland ecosystems and land conflicts with communities. Whereas deforestation rates in Indonesia have dropped markedly in recent years, the pulp and paper sector has not seen a transformation towards a No Deforestation, No Peatland, No Exploitation (NDPE) industry. Additionally, in terms of its structure, the sector is dominated by a handful of large and influential corporate actors. These are vertically integrated actors that operate industrial tree plantations, pulp mills and paper factories. They also have substantial influence over their suppliers. At the same time, a number of other industrial tree plantation owners operate in markets outside of the pulp and paper sector.
Aidenvironment has started a project to promote pulp and paper sector transformation by (1) creating near-real time transparency on deforestation, corporate ownership and supply chain relations; (2) introducing business risk concepts to enhance strategic engagement with influential stakeholders; (3) calling for cross-commodity implementation of NDPE policies of palm oil traders; and (4) developing influencing strategies that target key pulp and paper companies. Aidenvironment investigates and monitors a set of the most influential companies that either have leverage to change the sector, and/or that face particularly salient sustainability risks.
AidEnvironment news and insights
Our latest coverage on deforestation in the pulp and paper sector: five industrial tree plantation companies responsible for 3,000 ha of forest clearing first quarter 2022; fire alerts show the need for community engagement; four Indonesian pulp and paper companies responsible for 11,000 hectares of forest loss in 2021; and an op-ed piece titled “is there too much focus on palm oil?“